Some files & folders in the Windows system are difficult to clean up. Most of these files & folders are stubborn files & folders left on the hard disk after the program uninstallation. When you try to delete these files & folders manually, you will always get this prompt: "The file\folder is in use" or "Administrator privileges are required to delete". These files or folders not only take up computer storage space but also often interfere with user operations. How to delete these stubborn files & folders? Follow in the footsteps of WiseCleaner and discover solutions.
Method 1: Delete stubborn files & folders with Wise Force Deleter.
If you can't remember the command prompt instructions, force removal of software is also a good option.
Step 1: Run Wise Force Deleter.
If you have not installed Wise Force Deleter, please click the official download link: https://www.wisecleaner.com/wise-force-deleter.html.

Step 2: Add files or folders.
In Wise Force Deleter, there are two ADD buttons for you to choose from: Add file and Add folder. If files or folders are added by mistake, please click the button Remove.
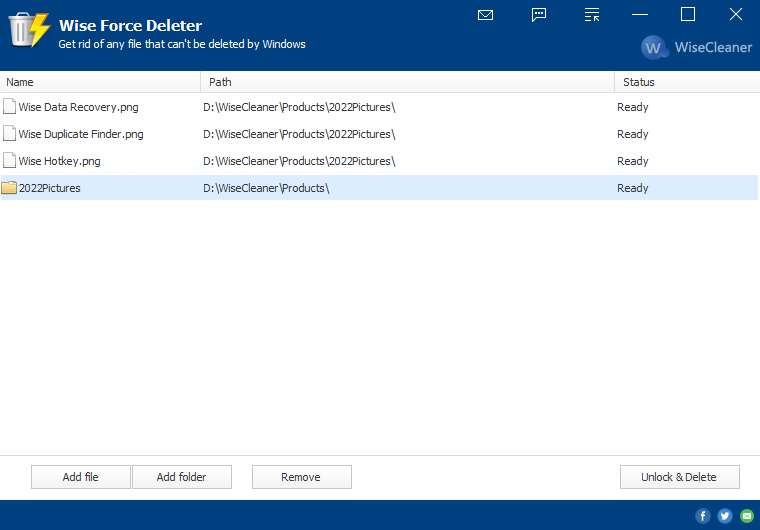
Step 3: Delete files & folders.
After confirming that the deleted files & folders are correct, click the Unlock & Delete button.
Method 2: Delete stubborn files & folders with Command Prompt.
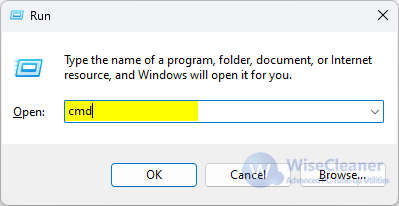
Step 1: Enable Command Prompt.
Press Win+r to open then Run window, then enter CMD and click OK to open Command Prompt.
Step 2: Enter the command to delete files & folders.
Users can delete files or folders from here.
1. Enter the command to delete the file.
The command format for deleting files is: del path of the folder to be deleted.
Here is an example of the file whose path is D:\WiseCleaner\Products\2022Pictures\Wise Care 365.png.
del D:\WiseCleaner\Products\2022Pictures\ WiseCare365.png
If you just want to delete a file within a folder, be sure to confirm that the path contains the name of the specific file. This means that the file name must contain the extension to be complete. If the file name does not contain an extension, the command prompt will display that the file cannot be found.
2. Enter the command to delete the folder
The format of the delete folder command is: del The path of the folder to be deleted.
Here is an example of a folder whose path is D:\WiseCleaner\Products\2022Pictures.
del D:\WiseCleaner\Products\2022Pictures
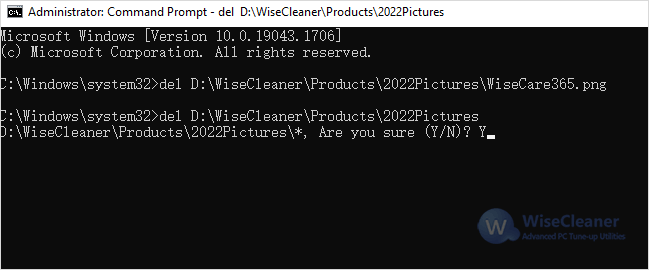
Then press Enter to confirm whether to delete the folder.
Y=Yes
N=No
After entering the command to delete the folder, the command prompt will empty all files in the folder.
Step 3: Check whether the files & folders are deleted.
Return the path of the deleted file & folder to check whether the file or folder has been deleted.
Conclusion
This article introduces readers to two easy-to-understand methods for deleting stubborn files or folders. One is to use the Windows system comes with components. The other is to use the computer force deletion software Wise Force Deleter. Both are effective solutions for deleting stubborn files or folders.