Task Types
Wise Auto Shutdown offers 6 different tasks could be chosen including Shut down, Restart, Log off, Hibernate, Sleep, and Lock screen.
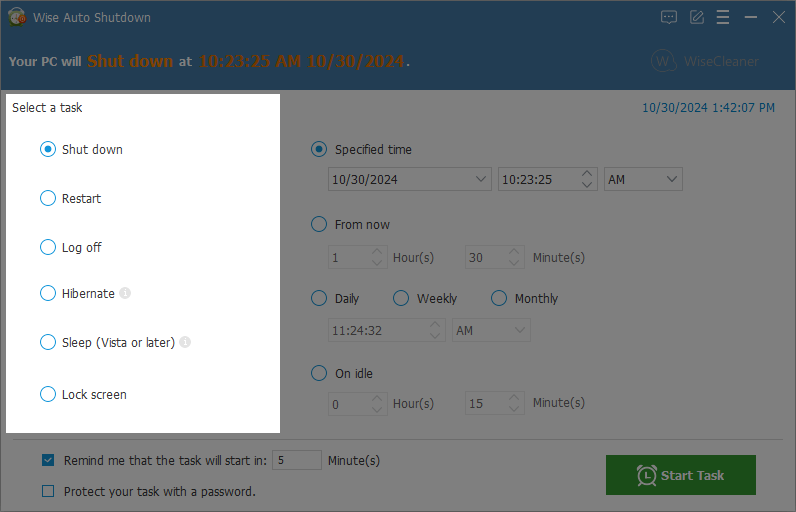
1. Shut down
When you select Shut down, your computer closes all open programs, along with Windows itself, and then completely turns off your computer and display. Shutting down doesn't save your work, so you must save your files first.
2. Restart
The Restart function in Windows is a crucial operation that allows you to close all running applications, refresh the operating system, and reinitialize the hardware and software components of your computer. Restarting can be necessary for various reasons, including installing updates, fixing issues, or simply refreshing the system's state.
3. Log off
When you log off from Windows, all of the programs you were using are closed, but the computer is not turned off.
After you log off, another user can log on without needing to restart the computer. In addition, you don't need to worry about losing your information if another user turns off the computer.
4. Hibernate
Hibernation is a power-saving state designed primarily for laptops. While sleep puts your work and settings in memory and draws a small amount of power, hibernation puts your open documents and programs on your hard disk, and then turns off your computer. Of all the power-saving states in Windows, hibernation uses the least amount of power. On a laptop, use hibernation when you know that you won’t use your laptop for an extended period and won't have an opportunity to charge the battery during that time.
5. Sleep
Aka Hybrid sleep, upgraded from legacy Sleep, is designed primarily for desktop computers. Hybrid sleep is a combination of sleep and hibernate—it puts any open documents and programs in memory and on your hard disk, and then puts your computer into a low-power state so that you can quickly resume your work. That way, if a power failure occurs, Windows can restore your work from your hard disk. When hybrid sleep is turned on, putting your computer into sleep automatically puts your computer into hybrid sleep. Hybrid sleep is typically turned on by default on desktop computers.
Legacy Sleep is a power-saving state that allows a computer to quickly resume full-power operation (typically within several seconds) when you want to start working again. It puts any open documents and programs in memory, then turn off your display and put your computer into a low-power state.
6. Lock Screen
The lock screen in a Windows operating system serves as a security feature that protects your computer while it is not in use. When you lock your screen, it prevents unauthorized access to your files and applications while allowing you to quickly resume your session when you return.
The primary purpose of the lock screen is to secure your device. When your computer is locked, anyone who tries to access it will need to provide the correct password, PIN, or biometric authentication (like a fingerprint or facial recognition) to unlock it.
Frequently asked questions
1. How to wake my computer from sleep or hibernation?
On most computers, you can resume working by pressing your computer's power button. However, not all computers are the same. You might be able to wake your computer by pressing any key on the keyboard, clicking a mouse button, or opening the lid on a laptop. Check the documentation that came with your computer or go to the manufacturer's website.
2. Will sleep eventually drain my laptop battery?
Sleep requires an extremely small amount of power—about the same as a nightlight. If your laptop battery charge gets critically low while the computer is asleep, Windows automatically puts the laptop into hibernation mode.
3. Is my data safe while my computer is asleep?
You can prevent unauthorized access by requiring a password to unlock your computer when it wakes from sleep.