| System Optimization |

Start by Optimization Wizard (recommended)
With this wizard, you can easy to tune up your PC without any professional knowledge.
Step 1: Welcome
Step 2: Choose your network

Step 3: Review the system information
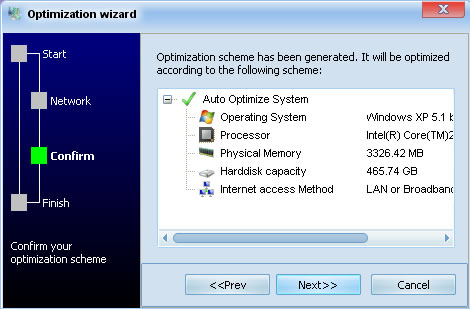
Step 4: Optimize your PC.
If you select Start by Advanced Settings, you can select the setting that the Optimize Wizard will use.
Start by Advanced Settings

Desktop Menu
Start Menu Speed.
Start menu speed optimization can make the start menu open faster. The user can adjust this
item to its best performance by using the regulating bar.
Menu Running Speed.
Menu running speed
optimization can improve the operating speed of all menus. The user
can adjust this item to its best performance by using the regulating bar.
Desktop Icon Cache.
Desktop icon
cache optimization can improve the display speed of the desktop icons. This
option is to set the maximum disk size for the system to put the icon cache
file into. Windows justification range is from 100KB to 4096KB, and the default value
is 500KB. If your desktop icons often get mixed up, we advise you to adjust it
to 2000KB. You can find the pre-set cache size when you open
this option, but you should not adjust this setting to a level less
than the size already in use.
Close visual effect such as an animation window, menu and list etc.
If you stop visual effects of windows you will lose some good visual effects, but with this tweak you can increase the speed a little.
Forbid recording running programs, used paths and documents
Forbid the system to keep records of used applications, paths and files. The selection of this option forbid the system from making records for history information and improve its performance. We advise you to select this option manually before using it to optimize the system.Use traditional Start Menu and Desktop for saving resources
Setting Windows to adopt the traditional start menu and desktop can save system
resources. If your PC's resources are poor, you are advised to use this option. (PS:
This option is only valid
to Windows XP and above)
Automatically restart Explorer in case of an exception occurring to Windows Explorer
If this option is chosen, Windows will restart
Windows Explorer automatically when there is unusual activity to explorer or
any of its components. We advise you to select this option. (PS:
This option is only valid for
Windows2000 and above)
Create independent process for Desktop and Explorer
Windows usually sets a multiple thread Explorer process
(including desktop, task bar, etc.) as default. This will
cause the crash of one thread to lead to the crash of all
other threads. This option will help to create independent
processes for desktop, task bar, etc.
If a Windows 9x user selects this option, the system will
pop out a "My Computer" window upon every startup, so we do
not advise you to select this option. Users of
Windows2000/XP/2003/Vista can select this option to improve
the system's stability. )

Disk Cache
This page provides some options for you to improve disk speed.
I/O Cache Size
The disk cache of Windows, virtual cache plays a very important role in system operation. Usually, Windows can auto-set the maximum memory to be its disk cache. However, virtual cache is a greedy system. Sometimes it takes up al the memory for its disk cache and frees part of the memory for other programs only when they apply for memory from Windows. So, it's necessary to set the disk cache size to save the time spent by the system calculating virtual cache and ensure the memory needs of other programs.
You can adjust the disk cache minimum value from 0 to 8192, maximum value from 0 to 40960 and cache read/write unit value from 0 to 4096 with the three regulating bars by entering the Window disk cache page. Based on different memory sizes, the optimization tool will give you proper prompts during your operation, but it should be pointed out that these prompts only fit standard users. Your values may vary.
Memory Performance
This option determines how Windows allocates memory.
1. Windows default value (Minimum
Memory Consume).
2. Windows will give
priority to allocate memory to the foreground application (Balance).
3. Windows will give
priority to allocate memory to the background program (Maximum Internet Through
puts (Recommend for Network Server).
Quick respond to application request
If this option is chosen, when a program is used in a window and asks for user input or for a focal point, its window will pop to the top.
Automatically close unresponsive applications
Program will be closed if it's detected as a non-responsive program.
Close waiting time
You can specify the amount of time it takes to close a non-responsive program. Set this time to 0, if a program has halted, it will be closed by windows immediately.
Waiting response time
How much time no response will be treated as non-responsive program.
Disable memory pages scheduling (More than 1 GB physical memory is recommended)
Normally Windows XP will write fragments of memory to the hard disk. We can prevent it from doing so, to keep data in the memory, because the speed of the memory is much higher than the speed of the hard disk, so it should be improve system performance. Users with large amounts of memory can use this setting. (More than 1 GB) (PS: This option is only valid for Windows XP and above)
Enable Large System Cache (Recommended to network Server)
This option enables the opening of a large amount of space
in the memory to save files in for future operation. If data applied by programs
increases, windows can help the programs to get the data in faster by
pre-reading the data first. PS:Enabling this option system cache will take up more
physical memory, and usable physical memory will be reduced. PC users or small
system users can get better file system performance after selecting this option,
but the overall performance of the system will be reduced heavily. What's more,
problems might occur on the hardware drive or in applications. Network servers
usually need more memory to buffer files, but PCs usually need more memory to
run programs, so we advise only network servers to choose this option. Some
software (e.g.. SQL Server, Exchange Server, etc.) will auto select this option
upon installation.)

Network
Internet connection selection
Modem. Users who connect to the Internet through a modem should select this option.
ISDN, i.e. Integrated Services Digital Network. Peak rate of N-ISDN (N: Narrow) can reach 64-128Kbps. According to our testing, the best rate of N-ISDN is only twice as fast as that of a 56K modem connection.
xDSL, i.e. Digital Subscriber Line. DSL includes symmetric IDSL, HDSL, SDSL and asymmetric ADSL, VDSL, etc. At present, there aren't many enterprises adopting DSL. PPPoE is the most common Internet access used by ADSL users. We advise DSL users to select this option.
PPPoE, Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet. At present this is the most common Internet access adopted by ADSL users, which can enable fast ADSL identity confirmation to create virtual digit dialing connection for users through PPPoE technology and an ADSL Modem. We advise PPPoE ADSL users to select this option.
Cable Modem, i.e. data sharing connection through CATV network. Users of Cable TV network Internet access should select this option.
LAN or broadband. This option is provided to LAN users who want to improve broadband performance. The most common bottleneck of a broadband connection for LAN users does not lie in the user’s system but on the outlet of the broadband supplier, which is caused by your district broadband design. (Description of district broadband design: 1. District broadband supplier rents broadband from telecoms or other companies; 2. broadband supplier lays fast channels such as fiber optic between rented server and districts; 3. Users connect to district server through LAN. As stated above, the way for district users to connect to the Internet is: user PC->district node->server rented by supplier->Internet. So the first bottleneck of district user Internet access speed lies in the size of the rented server; the second lies in the number of users.
Other connections. We suggest users of new Internet access (e.g. wireless connection to the Internet) select this option.
Maximum Transmission Unit:
This option defines the size of the largest protocol data unit (packet) in every frame.
Maximum data Segment Size
This option defines the actual segment size in the packet (datagram discussed in MTU). Because the packet includes information such as the IP address, MSS shouldn't exceed MTU in size. Standard IP header is 40, so both transferable MTU and MSS are 40.
Transmission Unit Buffer
This option defines the size of the maximum TCP receiving window of the system. The size of the window implies the transferable bytes when it hasn't received a response (Note: Refer to TCP/IP agreement for details about receiving window). If the transmission unit cache is set too small, transmission efficiency will be lowered because it may result in packet block. If the transmission unit is set too large, transmission efficiency will also be lowered because the error in one packet can lead other packets to be given up or re-sent.
Default package
This option has defined the default TTL for the header of the output IP message. IP packet will be discarded if it fails to reach its destination within the TTL. Windows default setting of TTL is 128.
Make windows browser "My Network Places" faster
By default, when a user tries to access My Network Places, Windows must first refresh all the available on-line neighbors, which takes more time. This option will disable Windows and try to refresh all available on-line neighbors to improve the access speed.
Optimize COM port buffer, port to be optimized: COM1
This option is to set the cache size for the COM port which the modem connects to. When this option is selected, Windows will auto-check the port connecting to the modem and define the proper cache size according to your memory size. Meanwhile, the optimization tool will set the band rate of the port as 115200.
Maximum threads connected by IE:
Optimize maximum thread number of IE simultaneous connection. For server HTTP 1.0, Windows restricts the maximum number of simultaneous connections to 4; For server HTTP 1.1, Windows restricts the maximum number of simultaneous connections to 2. The selection of this option will add IE simultaneous connections by way of adding server connections.

File System
Optimization Settings of CD/DVD-ROM
This optimization tool provides users with the most accurate CD/DVD-ROM access method on the basis of your memory size and hard disk size. For non-virtual CD-ROM users, it is recommended that you adjust the regulating bar to "Wise Registry Cleaner Recommended Value." Virtual CD-ROM users must adjust the regulating bar to its maximum value. (PS: This option is only valid for Windows 9x/me/2000/XP/2003).
There are 4 settings here.
1. Not Optimized
2.
Do not pre-read
3. Four-times speed or
faster
4: Recommended
Optimize the size of contiguous files and multimedia applications
When an application needs to call on a lot of files, the run speed of the application will be very slow. If enabled, this option??? windows will allow the application load more files at the same time, and it will run faster.
Automatically unloading unused DLL
Enables DLLs to auto-release physical memory when they are idle. Users with less memory are recommended to select this option to save more physical memory for other applications to use. (PS: This option is only valid for Windows 9x)
All Windows to optimize the hard disk in the background when idle
We suggest users select this option. (PS: This option is only valid for Windows XP/2003/Vista/7).
Close auto debugging function
In the Windows default setting, the system will assign debugging tools to debug when any errors happen (e.g. Dr Watson. Note: When a user has installed development tools such as Microsoft Visual Studio or msdev, etc.). Sometimes debugging tools can be a danger to the system because they consume extra system resources. We suggest that you disable the auto-debugging function of the debugging tools.
Allow Windows auto optimization to start partition
This option can let Windows auto-optimize the startup partition when the system needs it. We suggest users select this option. (PS: This option is only valid for Windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista/7).
Allow Windows auto reboot when Windows has crashed. (Blue Screen)
Enable this option when windows has crashed. (Blue screen and shows you an error message.) Windows will reboot automatically.

Boot Speed
Pre-read Method
This item only works in Windows XP/2003/Vista/7. Users can set the following four system pre-read methods: Disabled, Application Load Pre-read and System Startup Pre-read or both of the last two. If you select "Application Load Pre-read", you may reduce the times or the time of rolling scroll bars because the system does not pre-read files or indexes. We advise that you choose this option.
(After Windows XP, when windows boots, it will pre-read common applications and boot data. It takes more time to boot.)
Disable
Do not pre-read. (It will get fastest boot speed, however, some common applications will run slower.)
Application Launch Prefetching (Recommend)
Only pre-read application.
Boot Prefetching
Only pre-read boot data.
Both Prefetching
Windows default value. - Per-read applications data and boot data.
Start Waiting time disk error check in
If Windows has been shut down unexpectedly, in the next boot windows will check for disk errors. This option allows you to set: How long to wait before checking disk errors.
Auto Run upon Startup manager
This will allow you to select and deselect the programs that run when you startup your PC.
Recommend
Sets the settings to our recommendations.
Apply
Optimizes your PC.
Restore
Restores your original settings.
Close
Close this dialogue.
